|
1. General Overrunning
(超速運轉功能)
|
|
| Clutches used in this
type of application overrun at either the inner or outer race during
the majority of the clutch operating time and are occasionally called
upon to lock up and drive. A typical application is a two - speed
drive where an electric motor and a geared motor are connected to
a single driven shaft through one-way clutches. The machine can
be driven by either the electric motor or geared motor. When the
geared motor drives at low speed, the clutch engages. When the electric
motor drives the machine, the clutch overruns. The clutch automatically
switches between low speed and high speed. |
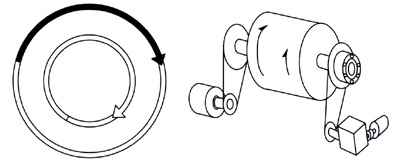 |
|
2. Indexing ( 分度 ,
定位功能)
|
|
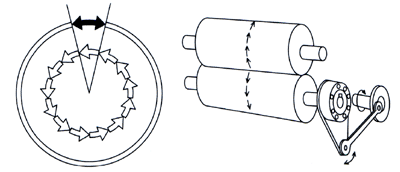
| In this mode of operation,
reciprocating motion applied to the driving race of the clutch is
transformed into unidirectional intermittent motion of the driven
race. For example, on a feeding roller, the clutch is mounted on the roller and a torque arm is connected to the driving race of the clutch. A crank motion mechanism provides reciprocating motion to the driving race. The clutch drives in the forward stroke (index) and overruns on the return stroke resulting in intermittent unidirectional motion of the feeding roller. |
 |
|
3. Backstopping (防止逆轉功能)
|
|
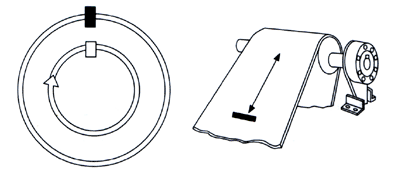
| In backstop (holdback)
applications, the clutches are used to prevent reverse rotation
of drive shafts and damage to machinery and other expensive equipment.
With the outer race of the clutch anchored to a stationary member, the inner race can overrun freely in one direction of rotation. Reverse rotation is instantaneously prevented by the automatic engagement of the clutch. Typical backstop applications are in conveyor systems and gear reducers. |
 |